Introduction
The four-stroke petrol engine is a fundamental component in the world of automobiles, powering millions of vehicles globally. This guide aims to provide a detailed understanding of how this engine works, its key components, and its importance in automotive engineering. Whether you're a student, professional, beginner, or advanced learner, this post will enhance your knowledge of four-stroke petrol engines.
What is a Four-Stroke Petrol Engine?
A four-stroke petrol engine is an internal combustion engine that completes a power cycle with four distinct strokes: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. Each stroke is a critical phase in the engine's operation, contributing to the efficient conversion of fuel into mechanical energy.
Key Components of a Four-Stroke Petrol Engine
- Cylinder: The core of the engine where fuel combustion occurs.
- Piston: Moves up and down within the cylinder, driven by the expanding gases from fuel combustion.
- Crankshaft: Converts the piston's linear motion into rotational motion, driving the vehicle's wheels.
- Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valves.
- Valves: Regulate the flow of air and fuel into the cylinder and exhaust gases out of the cylinder.
- Spark Plug: Ignites the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder
How a Four-Stroke Petrol Engine Works
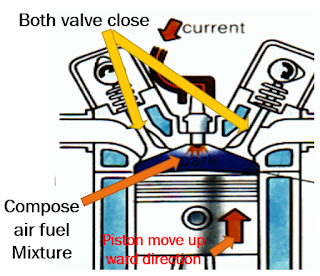
- Intake Stroke: The intake valve opens, and the piston moves down, drawing in a mixture of air and fuel into the cylinder.
- Compression Stroke: The intake valve closes, and the piston moves up, compressing the air-fuel mixture.
- Power Stroke: The spark plug ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture, causing an explosion that forces the piston down.
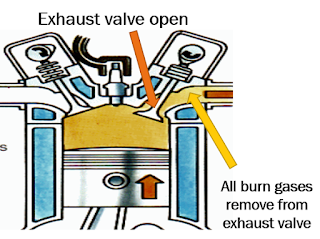
- Exhaust Stroke: The exhaust valve opens, and the piston moves up, expelling the burnt gases from the cylinder.
Advantages of Four-Stroke Engines
- Efficiency: More fuel-efficient compared to two-stroke engines due to better fuel combustion.
- Durability: Less wear and tear as each part completes fewer cycles.
- Environmental Impact: Produces fewer emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Performance: Provides a smoother and more controlled power delivery.
Example of a Four-Stroke Engine in Action
Case Study: Improving Performance with Regular Maintenance
- Initial Condition: A car with a four-stroke engine experiencing reduced fuel efficiency and power.
- Action Taken: Regular maintenance, including oil changes, spark plug replacement, and air filter cleaning, was performed.
- Results: The engine showed significant improvements in fuel efficiency, power, and overall performance.
Important Points to Remember
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and performance of a four-stroke engine.
- Fuel Quality: Using high-quality fuel can enhance engine performance and reduce wear.
- Oil Changes: Regular oil changes are essential to keep the engine components lubricated and functioning properly.
- Tune-Ups: Periodic engine tune-ups can help identify and resolve issues before they become major problems.
Conclusion
The four-stroke petrol engine remains a cornerstone of automotive engineering, offering efficiency, durability, and performance. By understanding its operation and maintaining it properly, students, professionals, and car enthusiasts can ensure their vehicles run smoothly and efficiently.




%20(11).png)
%20(7).png)
%20(5).png)
%20(10).png)

0 Comments